
| Documentation | User Forum | Developer Slack | WeChat |
Latest News 🔥
- [2026/02] We released 0.14.0 - This is the first stable release of vLLM-Omni that expands Omni’s diffusion / image-video generation and audio / TTS stack, improves distributed execution and memory efficiency, and broadens platform/backend coverage (GPU/ROCm/NPU/XPU). It also brings meaningful upgrades to serving APIs, profiling & benchmarking, and overall stability. Please check our latest paper for architecture design and performance results.
- [2026/01] We released 0.12.0rc1 - a major RC milestone focused on maturing the diffusion stack, strengthening OpenAI-compatible serving, expanding omni-model coverage, and improving stability across platforms (GPU/NPU/ROCm), please check our latest design.
- [2025/11] vLLM community officially released vllm-project/vllm-omni in order to support omni-modality models serving.
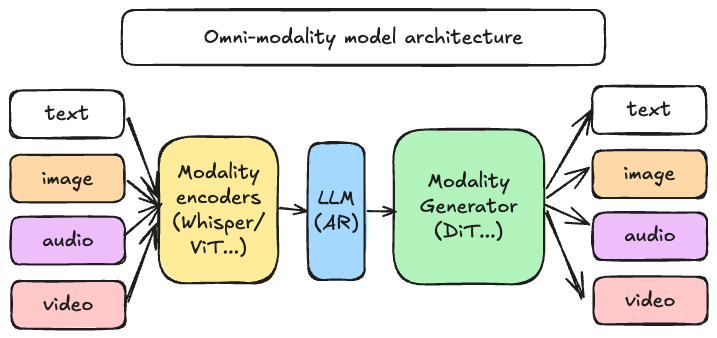
vLLM was originally designed to support large language models for text-based autoregressive generation tasks. vLLM-Omni is a framework that extends its support for omni-modality model inference and serving:
- Omni-modality: Text, image, video, and audio data processing
- Non-autoregressive Architectures: extend the AR support of vLLM to Diffusion Transformers (DiT) and other parallel generation models
- Heterogeneous outputs: from traditional text generation to multimodal outputs
vLLM-Omni is fast with:
- State-of-the-art AR support by leveraging efficient KV cache management from vLLM
- Pipelined stage execution overlapping for high throughput performance
- Fully disaggregation based on OmniConnector and dynamic resource allocation across stages
vLLM-Omni is flexible and easy to use with:
- Heterogeneous pipeline abstraction to manage complex model workflows
- Seamless integration with popular Hugging Face models
- Tensor, pipeline, data and expert parallelism support for distributed inference
- Streaming outputs
- OpenAI-compatible API server
vLLM-Omni seamlessly supports most popular open-source models on HuggingFace, including:
- Omni-modality models (e.g. Qwen-Omni)
- Multi-modality generation models (e.g. Qwen-Image)
Visit our documentation to learn more.
We welcome and value any contributions and collaborations. Please check out Contributing to vLLM-Omni for how to get involved.
If you use vLLM-Omni for your research, please cite our paper:
@article{yin2026vllmomni,
title={vLLM-Omni: Fully Disaggregated Serving for Any-to-Any Multimodal Models},
author={Peiqi Yin, Jiangyun Zhu, Han Gao, Chenguang Zheng, Yongxiang Huang, Taichang Zhou, Ruirui Yang, Weizhi Liu, Weiqing Chen, Canlin Guo, Didan Deng, Zifeng Mo, Cong Wang, James Cheng, Roger Wang, Hongsheng Liu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2602.02204},
year={2026}
}Feel free to ask questions, provide feedbacks and discuss with fellow users of vLLM-Omni in #sig-omni slack channel at slack.vllm.ai or vLLM user forum at discuss.vllm.ai.
Apache License 2.0, as found in the LICENSE file.